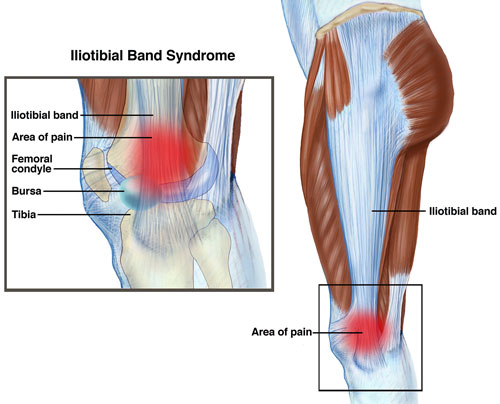
Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS)
ITBS (Iliotibial band syndrome) is one of the most common overuse injuries in distance runners. It occurs when the iliotibial band, the ligament which runs down from the hip to the tibia (shin bone) on the outside of the thigh, becomes inflamed or tightened.
The IT band attaches to the knee and helps in stabilizing and moving the joint. When the Iliotibial band is not working properly, the movement of the knee (running) becomes painful. Therefore, the pain in the Iliotibial band can be severe enough that a runner can be completely sideline for weeks or even longer.
Symptoms of Iliotibial Band Syndrome
The symptoms of Iliotibial Band Syndrome include pain on the outside (lateral) part of the knee, more specifically at or around the femur’s lateral epicondyle. The pain may return after a period of rest when you resume running.
After a period of rest, the pain may subside only to return when you resume running again. The pain is usually aggravated by running, especially in downhill running. The pain can be felt when flexing and straightening the knee, which may be made worse by pressing at the side of the knee over the sore area. There may be tightness in the IT band that runs down the outside of the thigh.
Your podiatrist or doctor may recommend or use Ober Test to assess this. Moving the leg out sideways or weakness in hip abduction is another common sign. Tender trigger points in the buttocks or gluteal muscles area may also be present.
Causes of Iliotibial Band Syndrome
The Iliotibial band Syndrome may result from any situation (activity) which causes the leg to turn inwards repeatedly. This can include running for too long, running downhill, wearing worn-out shoes, or running too many track workouts in the same direction.
However, unlike various overuse injuries, ITB(Iliotibial band) pain afflicts seasoned runners almost as much as beginners. When the IT band comes close to the knee, the band becomes narrow & rubbing (friction) can occur between the bone and band, this causes swelling and inflammation.
Treatment for Iliotibial Band Syndrome
The ITB (Iliotibial band) friction syndrome treatment needs to combine several options. The main goal is to reduce inflammation and pain, then stretch and condition the muscles so the injury doesn’t reoccur when returning to full fitness.
Some treatment methods include
Rest
It is essential to rest as it allows the tendon that is inflamed to get heal. If you continue to run in the presence of Iliotibial band syndrome, it will most likely make it worse. In the beginning, taking a complete rest is a good idea, but later activities other than running that do not make the pain worse, like cycling or swimming, are recommended to maintain fitness.
Cold Therapy
Apply ice or cold therapy to reduce swelling & inflammation. Ice should be applied for 10 minutes on the injured area (swelling part) followed by removal of ice for 20 minutes and repeat this treatment once or twice on the injured knee. Try to restrict the application of ice after 2 days or as soon as your swelling subsides.
Once the inflammation and swelling have gone, other potential causes must be addressed, such as a tight IT band, or the pain will most likely come back.
Stretching Exercises
In particular, stretching exercises of the muscles located on the outside of the hip are important. The tensor fascia late muscle is the muscle located at the top of the IT band, and if it is tight, it could cause the IT band to be tight, increasing the friction at the side of the knee.
Foam Roller Exercises
A foam roller applied to the gluteal and IT band muscles can help remove any tight lumps or knots in the tendon and help stretch the iliotibial band.






More Stories
Dynamic Polarity
Why Sugar Hacked Science (And Your Health!)
Mental Health – Depression